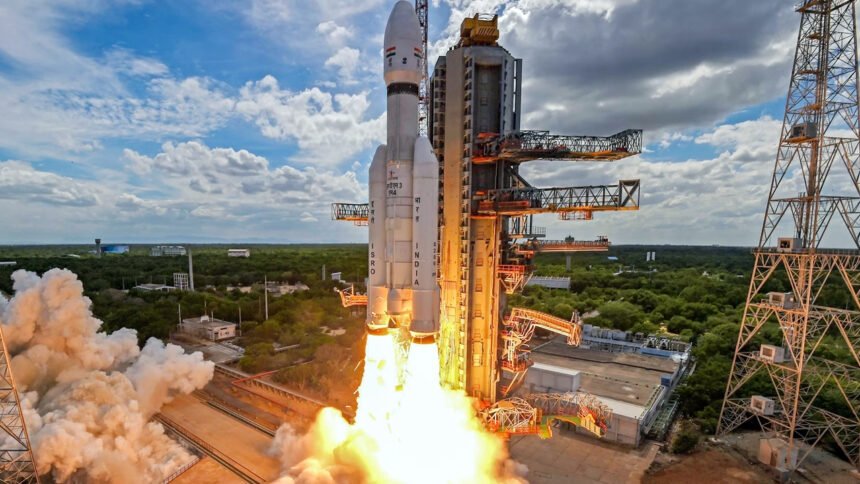
ISRO marked the beginning of the new year by successfully launching the PSLV-C58 X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) on January 1, 2024. This mission, the 60th for the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), commenced at 9:10 a.m. from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota. Within 22 minutes, the PSLV-C58 placed the XPoSat into a low inclination orbit to the east.
ISRO Chairman S. Somnath announced the achievement, stating, “On January 1, 2024, yet another successful mission of the PSLV has been accomplished. The PSLV-C58 has positioned the primary satellite, XPoSat, in the desired orbit of 650 km with a six-degree inclination.”
XPoSat represents ISRO’s maiden scientific satellite dedicated to conducting research on space-based polarization measurements of X-ray emissions from celestial sources. It incorporates two payloads: POLIX (Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays) developed by the Raman Research Institute (RRI) in Bengaluru, and XSPECT (X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing) developed by the Space Astronomy Group of URSC, Bengaluru.
This successful launch propels India into an exclusive category, making it the second nation to deploy an observatory specifically designed to study astronomical phenomena such as black holes and neutron stars.
During the mission, the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-3 (POEM-3) experiment was executed to meet the objective of ten other payloads. Following the injection of XPoSat into a 650 km, 6-degree orbit, the PS4 stage was lowered to a 350 km, approximately 9.6-degree orbit by restarting it twice. The PS4 stage functions as a 3-axis stabilized orbital platform for conducting experiments with space-qualified systems featuring novel ideas.
Additionally, the PSLV launched ten payloads developed by start-ups, educational institutions, and ISRO centers. These include the Radiation Shielding Experimental Module (RSEM) by TakeMe2Space, Women Engineered Satellite (WESAT) by LBS Institute of Technology for Women, BeliefSa-t0 Amateur radio satellite by K.J. Somaiya Institute of Technology, Green Impulse TrAnsmitter (GITA) by Inspecity Space Labs Private Limited, Launching Expeditions for Aspiring Payloads – Technology Demonstrator (LEAP-TD) by Dhruva Space Private Limited, RUDRA 0.3 HPGP by Bellatrix Aerospace Private Limited, ARKA-200 by Bellatrix Aerospace Private Limited, Dust Experiment (DEX) by PRL, ISRO Fuel cell Power System (FCPS) by VSSC, ISRO, and Si-based High Energy cell by VSSC, ISRO.